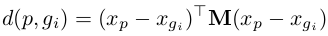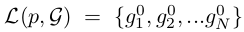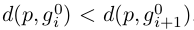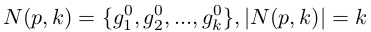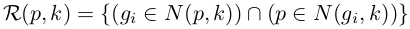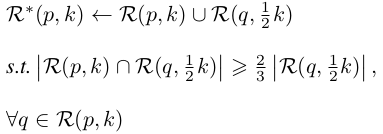CVPR2017
Re-ranking Person Re-identification with k-reciprocal Encoding

Abstract
当将person re-ID看作一个检索过程时,re-ranking是提高其准确性的关键步骤。然而,在re-ID社区中,对re-ranking的努力有限,尤其是那些全自动、无监督的解决方案。在本文中,我们提出了一种k-reciprocal编码方法来re-ranking re-ID的结果。我们的假设是,如果一个gallery图像与k-reciprocal nearest neighbors中的probe查询相似,则更有可能是真正的匹配。具体地,给定图像,通过将其k-reciprocal nearest neighbors编码为单个向量来计算k-reciprocal特征,该向量用于在杰卡德距离(Jaccard Distance:用来衡量两个集合差异性的一种指标)下re-ranking。最终的距离计算为原始距离和杰卡德距离的组合。我们的re-ranking方法不需要任何人工交互或任何标记数据,因此适用于大规模数据集。在大型Market-1501、CUHK03、MARS和PRW数据集上的实验证实了我们方法的有效性。
Introduction
person re-ID是计算机视觉中的一个具有挑战性的课题。一般来说,re-ID可以被看作是一个检索问题。给定一个probe person,我们希望在gallery中搜索包含处于跨相机模式下的相同行人的图像。在获得初始排序列表之后,好的实践包括添加re-ranking步骤,期望相关图像将获得更高的排名。因此,本文将重点放在re-ranking问题上。
re-ranking主要是在通用实例检索generic instance retrieval[5、14、34、35]中进行研究。许多re-ranking主方法的主要优点是它可以在不需要额外训练样本的情况下实现,并且可以应用于任何初始ranking结果。
re-ranking的有效性在很大程度上取决于初始ranking列表initial ranking list的质量。许多先前的工作利用了初始排序列表[5,14,34,35,43,44]中排名靠前的图像(例如k-最近邻,k-nearest neighbors)之间的相似关系。一个基本的假设是,如果返回的图像在probe的k个最近邻内排序,那么它很可能是一个真正的匹配,可用于随后的re-ranking。然而,情况可能偏离最佳情况:错误匹配很可能包括在probe的k个最近邻中。例如,在图1中,P1、P2、P3和P4是4个查询图probe的真实匹配,但是它们都不包括在top-4中。我们观察到一些错误匹配(N1-N6)获得高排名。结果,直接使用top-k的图像可能在re-ranking系统中引入噪声并损害最终结果。
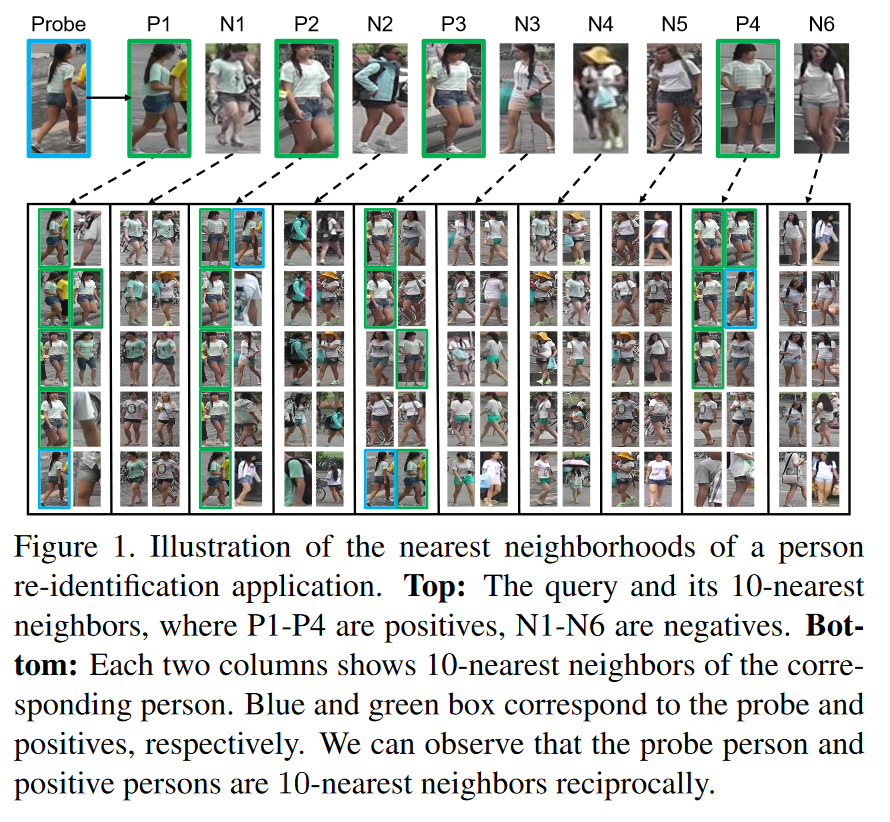
在文献中,k-reciprocal nearest neighbor[14,34]是解决上述问题的有效方法,即被错误匹配污染的top-k图像。当两个图像被称为k-reciprocal nearest neighbor时,当另一个图像作为probe时,它们都被排到top-k。因此,k-reciprocal nearest neighbor作为两个图像是否正确匹配的更严格规则。在图1中,我们观察到probe是正确匹配图像的reciprocal neighbor,而不是错误匹配图像的reciprocal neighbor。该观察识别初始排序列表initial ranking list中的正确匹配,以改善重新排序re-ranking结果。
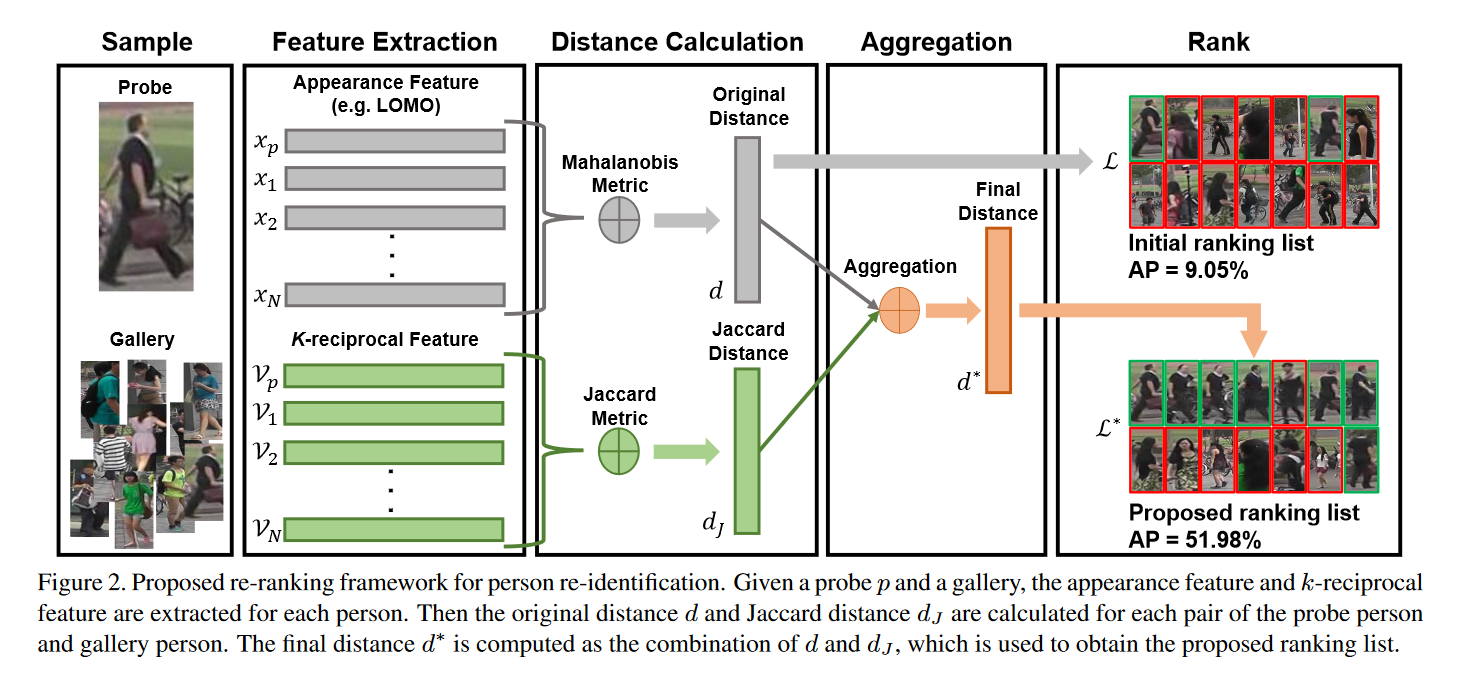
基于以上考虑,本文提出了一种基于k-reciprocal编码的re-ID re-ranking方法。我们的方法包括三个步骤。首先,将加权的k-reciprocal neighbor 集编码为一个向量,形成k-reciprocal特征。然后,两个图像之间的Jaccard距离可以通过它们的k-reciprocal特征来计算。其次,为了获得更鲁棒的k-reciprocal特征,我们改进了一种局部查询扩展方法(a local query expansion approach),以进一步改善re-ID性能。最后,最终距离的计算为原始距离和Jaccard距离的加权集合。随后,它被用来获取re-ranking列表。所提出的方法的框架如图2所示。综上所述,本文的贡献是:
- 我们提出了一个k-reciprocal特征通过编码k-reciprocal特征到一个单一的向量。重re-ranking过程可以很容易地通过向量比较来执行。
- 我们的方法不需要任何人工交互或带标注的数据,并且可以自动和无监督的方式应用于任何人person re-ID ranking结果。
- 该方法有效地提高了Market-1501、CUHK03、MARS和PRW等数据集上的person re-ID性能。特别地,我们在rank-1和mAP上实现了Market-1501的最先进的精度。
我们推荐感兴趣的读者阅读[3,50]以详细回顾person re-ID。在此,我们重点研究用于目标检索,特别是用于re-ID的re-ranking方法。
Re-ranking for object retrieval.
Re-ranking方法已被成功地研究以提高目标检索精度[51]。许多工作利用k-nearest neighbors来探索相似关系来解决re-ranking问题。[5]提出了average query expansion (AQE)方法,该方法通过对top-k返回结果中的向量进行平均,得到一个新的查询向量(query vector),用于对数据库进行重新查询。为了利用远离查询图像的负样本,Arandjelović和Zisserman[1]改进了discriminative query expansion (DQE),使用线性SVM来获得权重向量。从决策边界的距离被用来修改初始排序表(initial ranking list)。[35]利用初始排序表的k-nearest neighbors作为新查询(queries)来生成新的排序表。每个图像的新得分根据其在产生的排序表中的位置来计算。最近,稀疏上下文激活sparse contextual activation (SCA)[2]提出将neighbor set编码为向量,并通过广义Jaccard距离来表示样本的相似性。为了防止错误匹配对top-k图像的污染,[14,34]中采用了k-reciprocal nearest neighbors的概念。在[14]中提出了上下文不相似性度量contextual dissimilarity measure (CDM),通过迭代正则化每个点到其邻域的平均距离来细化相似性。[34]正式提出k-reciprocal nearest neighbors的概念。k-reciprocal nearest neighbors被认为是高度相关的候选,用于构造闭集(closed set)以re-ranking数据集的其余部分。我们的工作从两个方面背离了这两个方法。我们不像文献[14]那样对最近邻(nearest neighborhood)关系进行对称化来细化相似度,也不像文献[34]那样直接将k-reciprocal nearest neighbors看作高阶样本。相反,我们通过比较两幅图像的k-reciprocal nearest neighbors来计算它们之间的新距离。
Re-ranking for re-ID.
大多数现有的person re-ID方法主要集中于特征表示[41,12,23,48,21]或度量学习[23,17,9,32,45]。最近,一些研究者[10,33,28,24,49,20,11,19,42,44]已经注意到在re-ID社区中基于re-ranking的方法。[20]通过分析每对图像的近邻(near neighbors)的相关信息和直接信息,建立re-ranking模型。在[11]中,通过联合考虑排序列表中的内容和上下文信息,学习无监督的重新排序模型,有效地去除了模糊样本,提高了re-ID的性能。[19]提出一种双向排序(bidirectional ranking)方法,利用计算得到的新相似度作为内容相似度和上下文相似度的融合,对初始排序表进行修正。最近,利用不同基线(different baseline)方法的公共最近邻来re-ranking任务[42,44]。[42]将全局特征和局部特征的公共最近邻作为新查询(queries),通过集合全局特征和局部特征的新排序列表来修改初始排序列表。在[44]中,利用k-nearest neighbor set从不同的baseline方法计算相似度和不相似度,然后进行相似度和不相似度的集合来优化初始排序表。上述方法在re-ranking方面继续取得进展,有望为将来从k-nearest neighbors发现进一步的信息作出贡献。然而,使用k-nearest neighbors直接实现re-ranking可能限制整体性能,因为常常包括错误匹配。为了解决这个问题,本文研究了k-reciprocal neighbors在person re-ID中的重要性,从而设计了一个简单而有效的re-ranking方法。
Proposed Approach
Problem Definition
给定查询图像p和gallery set(包含N幅图像,G = {gi | i = 1, 2, ...N }),p和gi之间的原始距离可以用马氏距离(Mahalanobis distance)衡量:
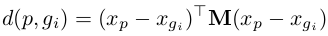
其中,xp个xg分别代表查询图p和检测集gallery中gi的外观特征,M是半正定矩阵。
初始排序表:
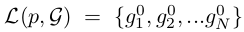
可根据probe p和gallery gi之间的成对原始距离得到,其中:
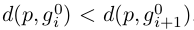
我们的目标是对L(p,G)进行re-rank,使更多的正样本排在top列表中,从而提高person re-ID的性能。
K -reciprocal Nearest Neighbors
我们将N(p,k)定义为一个probe p的k-nearest neighbors(i.e. 排序列表的top-k samples):
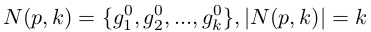
其中,|.|表示集合中候选的数目。k-reciprocal nearest neighbors R(p, k)可以定义为:
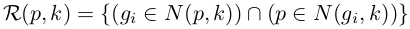
根据前面的描述,k-reciprocal nearest neighbors比k-nearest neighbors和probe p更相关。然而,由于照明、姿态、视图和遮挡的变化,正样本图像可能被从k-nearest neighbors中排除,并且随后不被包括在k-reciprocal nearest neighbors中。为了解决这个问题,我们根据以下条件将R(p,k)中每个候选项的1/2 k-reciprocal nearest neighbors增量地添加到更鲁棒的集合R*(p,k)中:
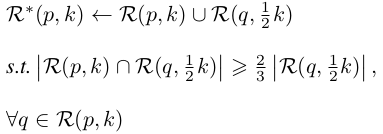
Conclusion
在本文中,我们解决person re-ID的re-ranking问题。通过将k-reciprocal nearest neighbors编码为单个向量,我们提出了k-reciprocal特征,从而可以通过向量比较容易地执行re-ranking过程。为了从相似样本中获取相似关系,提出了局部扩展查询(local expansion query)以获得更鲁棒的k-reciprocal特征。基于原始距离和Jaccard距离的组合的最终距离有效地提高了多个大规模数据集上的re-ID性能。值得一提的是,我们的方法是全自动和无监督的,并且可以很容易地实现任何ranking结果。